Applications
the Art of Solution ℠
Solutions • Performance • Partners
Lysartis, Inc. leverages our proprietary matrix development platforms to provide our customers with porous flat sheet material solutions. Our services include guidance on material selection, prototyping, small scale manufacture, and full-scale manufacture including complete validation, technology transfer and licensing.
Here you will find examples of projects we have completed to highlight the breadth and scope of our capabilities.
Not your standard catalogue offering
m - PES Micro-filtration Membranes
Using our proprietary membrane production platform, we offer specific grade development for micro-filtration applications, with effective pore sizes ranging from 0.01 μ to 50 μ.
The m-PES micro-porous matrix has an anisotropic cross section structure, with the selective layer inside the bulk of the cross-section.
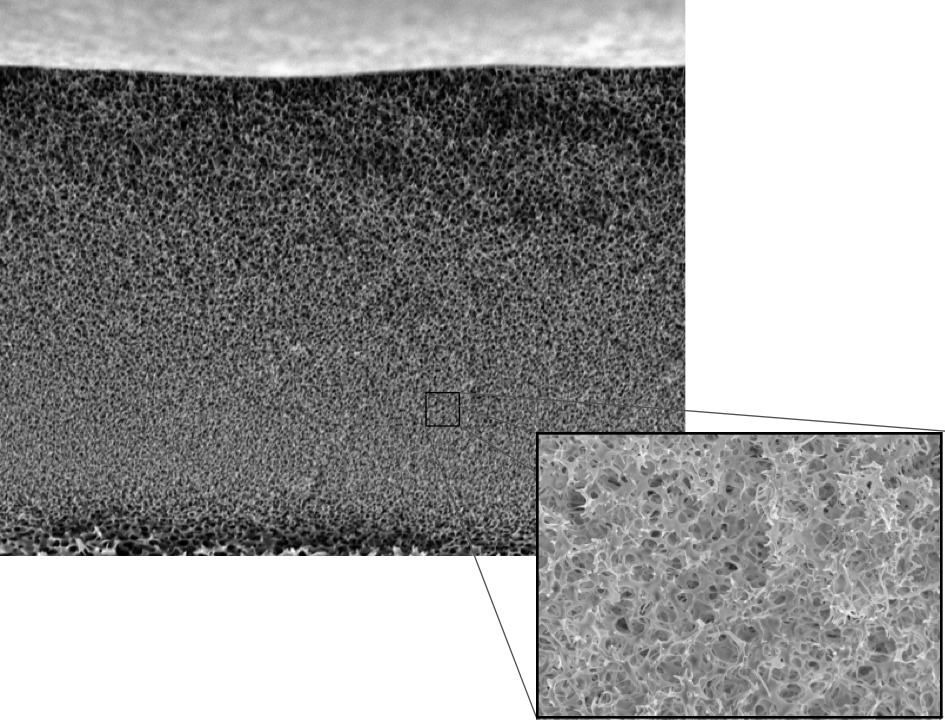
(Cross-sectional SEM mag. x 1,000, inset box is 20 μm in width, mag. x 10,000)
Mega micro better than meltblown
The choice of filter media is still broadly limited to an “either – or”: either “membrane” or “fiber matrix”, the decision being based primarily on solute size.
Fiber matrices are typically the first choice for large solutes ( ≥ 5 μm). However, when stringent log reduction requirements exist (for bacteria, yeast, sub micron particulate), membranes have been the media of choice.
Using our proprietary membrane production platform, we offer specific grade development for micro-filtration applications, with effective pore sizes ranging up to 50μm.
The advantages of selectivity and flow rate is now also available in membranes with large pore sizes.
The advantages of selectivity and flow rate is now also available in membranes with large pore sizes.
Membranes have tigther pore size distribtions.
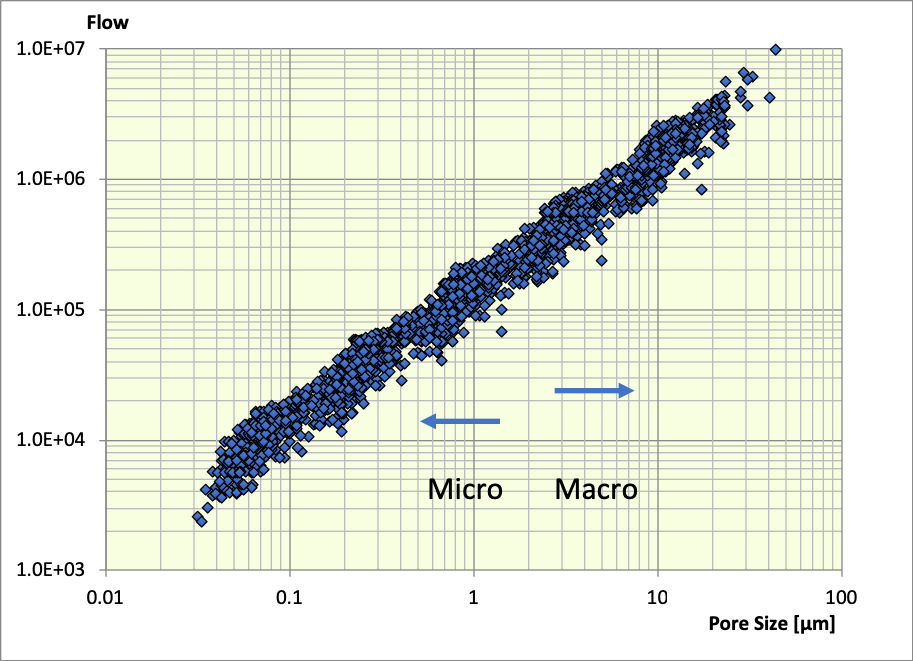
Membranes have better flow to pore size performance.
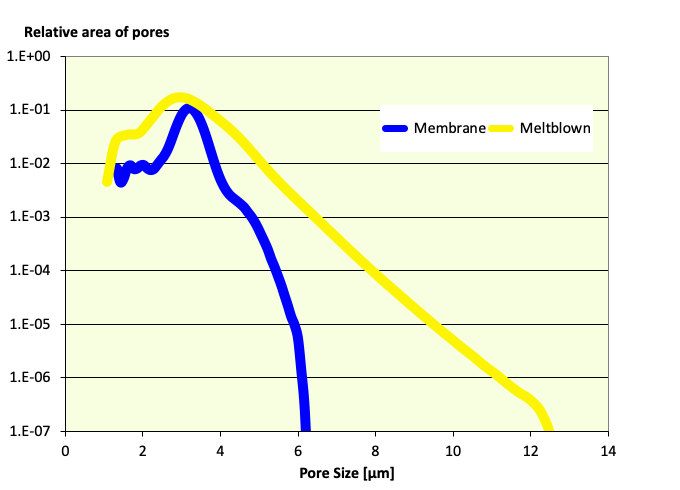
Pore size distribtion of Membranes and Meltblows of similar pore size
|
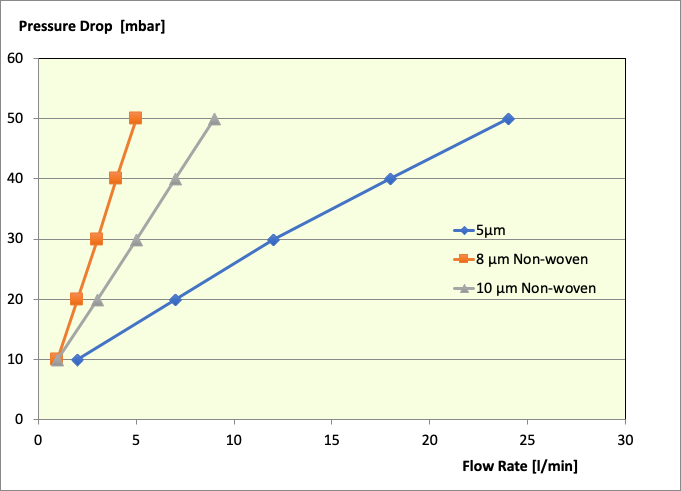
Permeabilities of Membranes and Meltblows of similar pore size
|
Carbohydrate rich waste stream processing
Food processing waste streams can have a wide variety of species present over a considerable size range. Regulatory requirements and the possibility of value added from recovery of waste components has led process developers to look at processing these streams. The first choice of a filter material of large solute sizes has been non-wovens. Lysartis works with process developers to evaluate the potential advantage of membranes in these applications. Such membranes would need to have pore sizes in the range of 20 to 50 μm. The flow advantages, combined with the selectivity of the membrane have shown that a high process performance was achieved using cast porous membranes compared to non-woven materials
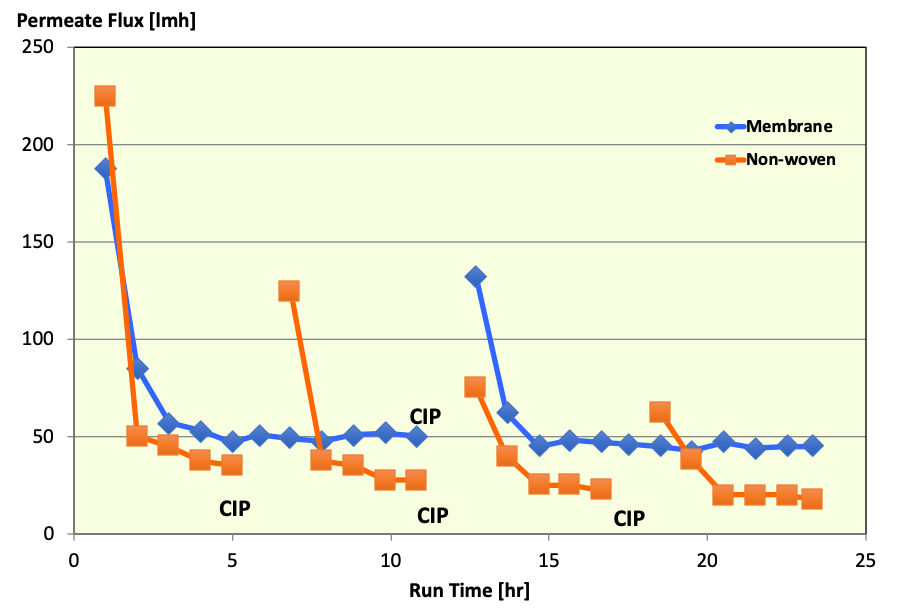
Membrane vs Calendared Non-Woven
Carbohydratte rich process waste
Both Membrane and Non-Woven had bubble pooint of 0.1 MPa / 1 psi
Such performance advantages have also been seen in more stringent application, such as the processing of bio-reactor product.
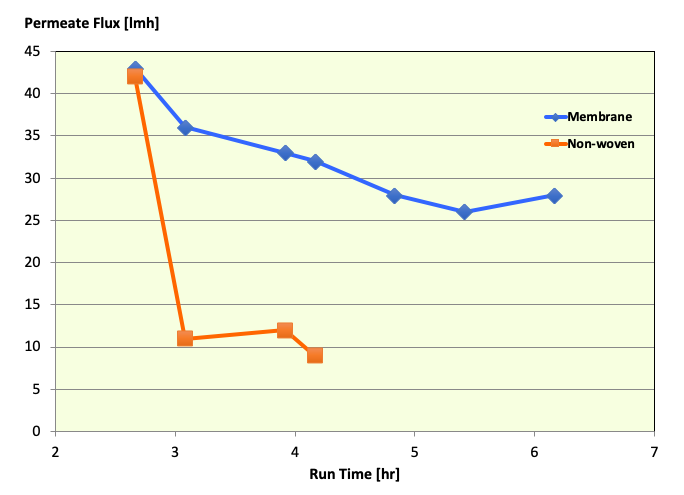
Fermentation broth for food/nutraceutical application
objective: retain whole cells and pass extracellular product
Both Membrane and Non-Woven had Bp of 0.7 MPa / 7 psi
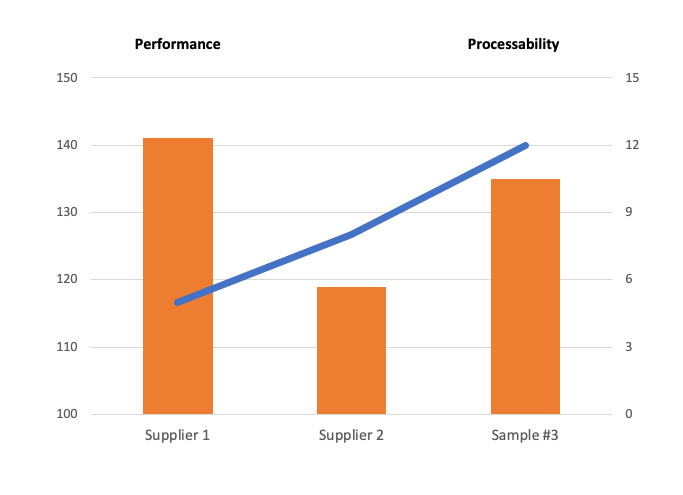
SUPER STRONG without LOSS of PERFORMANCE
Material process performance is not always the deciding factor of material's useability.
In most applications a material will be encapsulated in a holder of some kind so it can be used. Here the material's processability becomes the deciding factor in its useage.
Integrated Immuno-diagnostic test strip:
Wicking , blood filter and binding on one material
Immuno-diagnostic test strips, particularly in the lateral flow format, are complicated multi component constructions of sometimes poorly compatible materials needed to be physically interfaced to ensure functionality
An alternate, one material construction was conceived using a single substrate which performs multiple functions. Using a specially designed asymmetric matrix of non-binding polymer direct cast on a rigid backing:
It filters the red cells from the blood sample, to give clear serum,
via a micro-fluidic gate, it wicks the serum through an integrated conjugate zone.
It then wicks the sample to the test line zone, a localized area specifically activated to bind the captured antibodies
and continues to wick on into the end test reservoir.
Long Life Stored Micro-Array
A rugged, micro-array substrate with an indefinite archived shelf life has long been sought. Coated glass slide micro-array substrates are robust platforms. The active layers can however be delicate and prone to damage as a result of handling.
Taking the classic laboratory glass slide as base geometry, micro-array substrates were fixed in place. Useful materials such as nitro-cellulose, polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) and nylon were selected for evaluation, with nitro-cellulose proving to be the most versatile.
Microporous layers of nitro-cellulose were anchored onto the slides. Layers in the range of 5 μm to 20 μm were trialed. Optimization was required to refine spot capacity and geometry.
Spot optimization: E2S PCR DNA printed at 50 ng / μL Type #1212
|

Spot optimization: E2S PCR DNA printed at 50 ng / μL Type #0713
|
A fixing/transparency achieving procedure was developed to give the clarity and endurance. Suitable sensitivity was achievable with competitive signal to noise response, as demonstrated using mock hyribizations in comparison to other systems available.
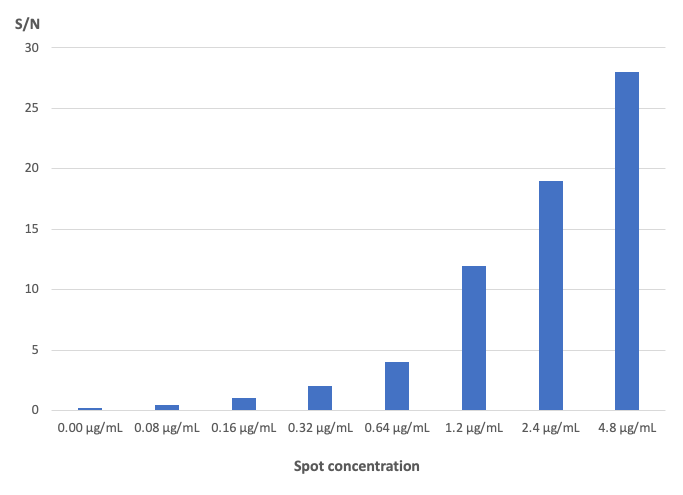
S/N study for dilution series of biotinylated BSA
|
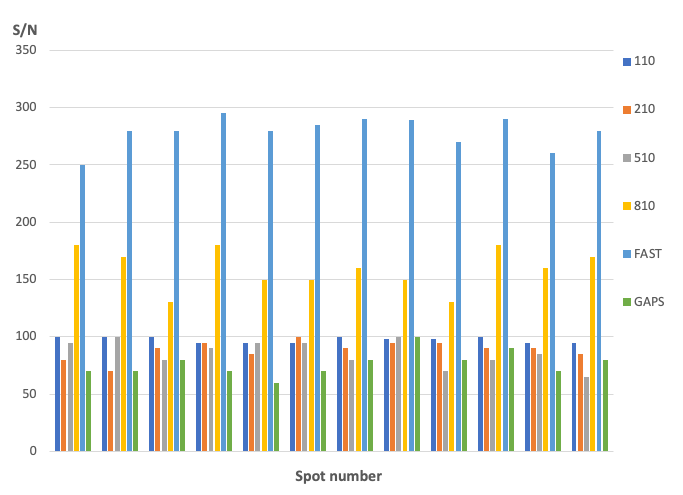
Array local background comparison after mock hybridization
|
We compared substrates using a more complex system – human placental cDNA detection of PCR DNA arrays. The sensitivity of the arrays and the efficacy of the archival system proved compatible with real world applications.
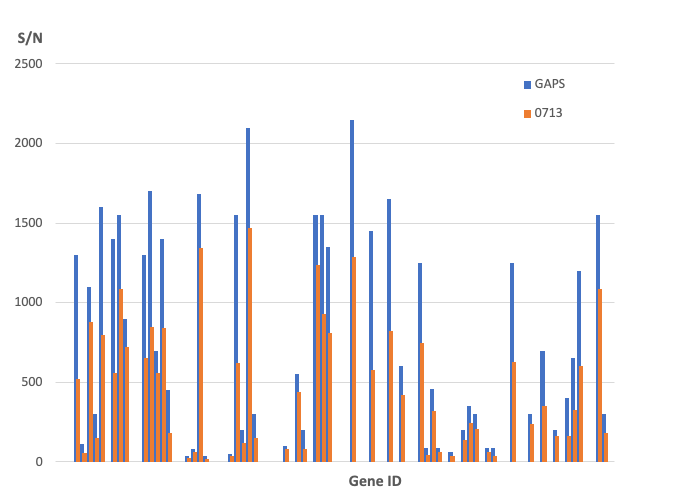
The achieved slides show required long term stability with the added advantage that the active array area is made both scratch and dent resistant.
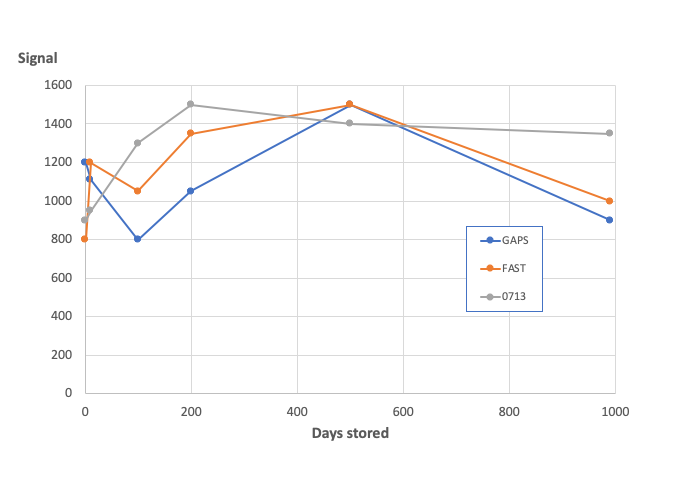
mirad | matrix #0713 , FAST & GAPS slides
The technology was also expanded to 96 well micro titer plate format.